Remove With Caution: root.txt -> /
Outline
If you have any experience with working with a CLI then you are hopefully familiar with tab autocomplete - or in my case spamming TAB as I type a command or directory path so that I don’t have to type it all out. It’s really helpful.
Unfortunately sometimes the tab autocomplete can make it easier for dangerous commands to be accidentally run.
Malicious symlink: root.txt -> /⌗
Let’s say we have this malicious symlink left behind by some malware on an individual website.
lrwxrwxrwx 1 www-data www-data 1 May 12 18:52 root.txt -> /
It’s a symlink from the server’s main / directory to a file named root.txt.
Tab Autocomplete Is Dangerous Here⌗
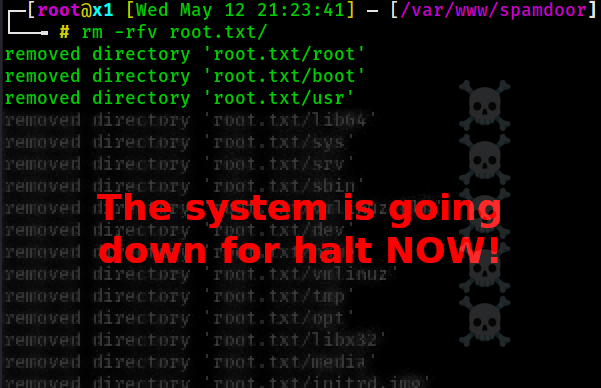
The problem is that when using tab autocomplete to finish the filename - it will add a trailing slash / to the filename as if it were a directory. This means it will follow the symlink file to its symlink destination, which is the server’s / directory.
This can lead to a careless mistake by a sysadmin and result in them running rm -rfv root.txt/ and that / is what will take down the server unless the admin is fast with CTRL + C.
─[root@x1 [Wed May 12 19:12:47] ─ [/var/www/spamdoor]
└──╼ # rm -rv root.txt/
removed directory 'root.txt/root'
removed directory 'root.txt/boot'
removed directory 'root.txt/usr'
removed directory 'root.txt/lib64'
removed directory 'root.txt/sys'
removed directory 'root.txt/srv'
removed directory 'root.txt/sbin'
removed directory 'root.txt/vmlinuz.old'
I’ve seen more than one sys admin make this mistake and take down over a thousand websites until backups could be restored.
I use one of the two commands to remove symlinks safely, but be sure not to remove any legit symlinks:
find . -type l -delete or unlink